Add and Index Git Data Sources
Connect and index Git repositories as data sources.
Git repositories are one of the most powerful data sources in AI/Run CodeMie, enabling assistants to analyze code, understand repository structure, and work with your codebase directly. This guide walks you through the process of adding and indexing Git repositories.
Prerequisites
This data source requires you to have at least one Git integration added to AI/Run CodeMie. For more details, please refer to the Integrations Overview guidelines.
Before adding a Git data source, ensure you have:
- Configured Git integration (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket)
- Access to the repository you want to index
- Appropriate permissions to access repository content
If you haven't configured a Git integration yet, follow the Integrations Guide first.
Adding a Git Data Source
To index a Git repository, fill in the following fields:
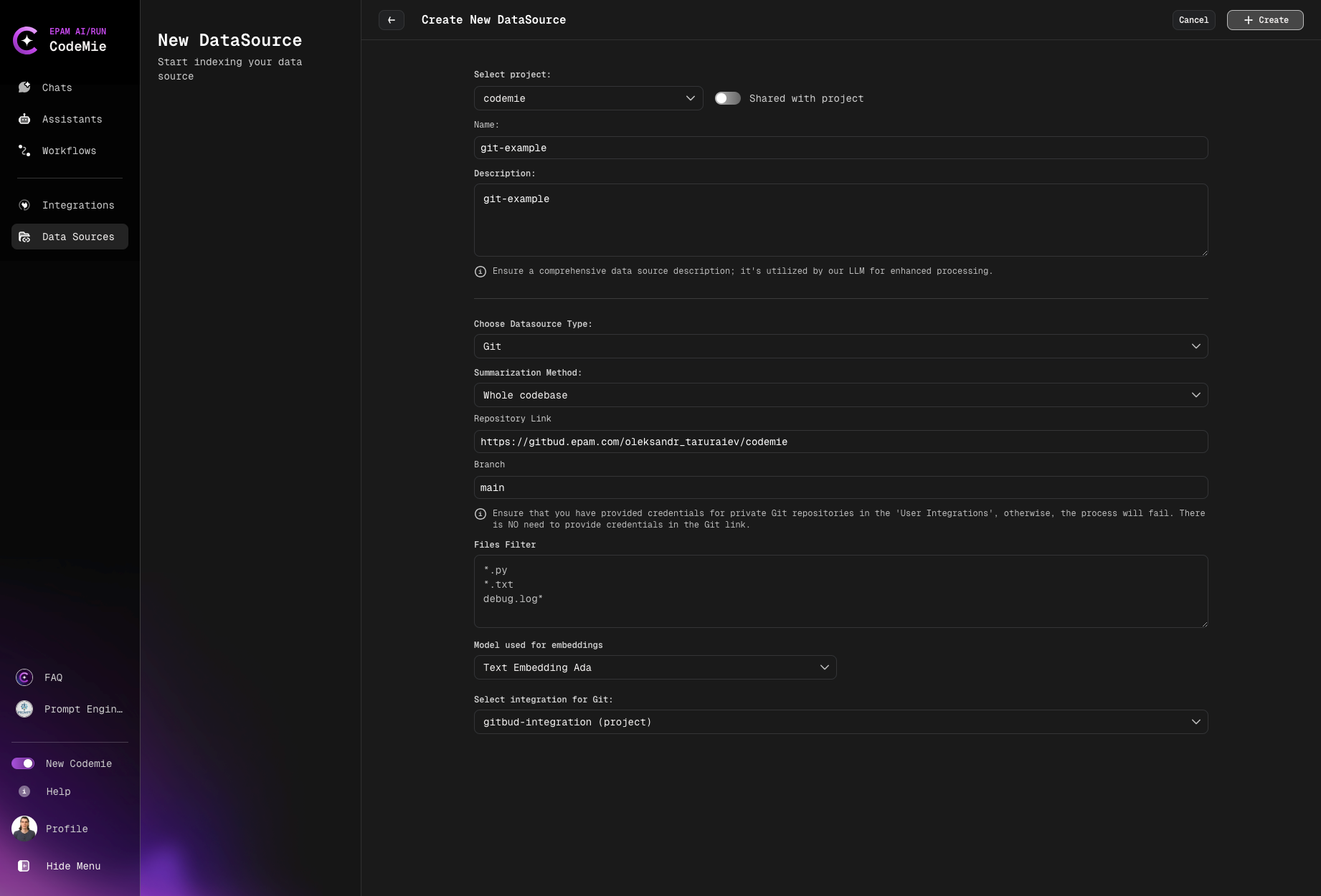
Configuration Fields
4. Select Source Type
- Select Project: Select the name of the project with which you want to associate that DataSource.
- Name: Alias for file for quick search in datasource list.
- Description: Description for this datasource
- Choose Datasource Type: Git source type in the add new data source window.
- Choose Available indexing types:
- Whole codebase
- Summarization per file
- Summarization per chunks
Direct indexing of raw code
- Best for: Quick setup, simple code analysis
- Use when: You want fast access to code without additional processing
Generates summaries for each file
- Best for: Documentation generation, code overview
- Use when: You need high-level understanding of codebase
Creates summaries for code chunks
- Best for: Large codebases, detailed navigation
- Use when: You need comprehensive code understanding
- Note: Preferred mode, takes approximately 30-60 minutes
- Whole codebase: Fast setup, ideal for small projects (< 500 files)
- Per file: Best for documentation and code overview
- Per chunks: Recommended for production use and large codebases
- Repository Link:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
https://github.com/username/repository
https://gitlab.com/username/repository
https://bitbucket.org/username/repository
- Branch: Specify the target branch to work with.
Always use stable branches (e.g., main, master, develop) for indexing. Feature branches may be deleted, breaking your data source.
- Files Filter: Specify relevant file extensions to index in the field.
Filter behavior:
- Empty filter: Include all files
- Patterns (e.g.,
*.py): Include ONLY matching files (whitelist) - !Patterns (e.g.,
!*.nupkg): EXCLUDE matching files (blacklist) - Combined (e.g.,
*.py,!test_*.py): Include .py files except test_*.py files
Examples:
- Python projects:
*.py- Only Python files - JavaScript/TypeScript:
*.js,*.ts,*.tsx,*.jsx- Only JS/TS files - Exclude binaries:
!*.nupkg,!*.dll,!*.exe- Exclude package and binary files - Java source only:
src/**/*.java- Only Java files in src directory - Python without tests:
*.py,!test_*.py,!*_test.py- Python files excluding tests - Documentation only:
*.md,*.rst,*.txt- Only documentation files
- Model Used for Embeddings: Select model Used for Embeddings.
- Select integration for Git: Choose integration.
5. Configure Reindex Schedule (Optional)
In the Reindex Type section, configure automatic reindexing:
- Scheduler: Choose your preferred reindexing schedule
- No schedule (manual only) - Default, requires manual reindexing
- Every hour - For rapidly changing repositories
- Daily at midnight - Recommended for most active repositories
- Weekly on Sunday at midnight - For stable repositories
- Monthly on the 1st at midnight - For rarely updated repositories
- Custom cron expression - Enter custom cron expression (e.g.,
0 9 * * MON-FRI)
6. Create Data Source
Click the + Create button and wait for the process to finish.
Initial indexing may take 15-60 minutes depending on repository size. You can close the page - indexing continues in the background.
What happens next:
- AI/Run CodeMie validates the configuration
- Connection to repository is established
- Indexing process begins automatically
- Progress can be monitored in the data source list
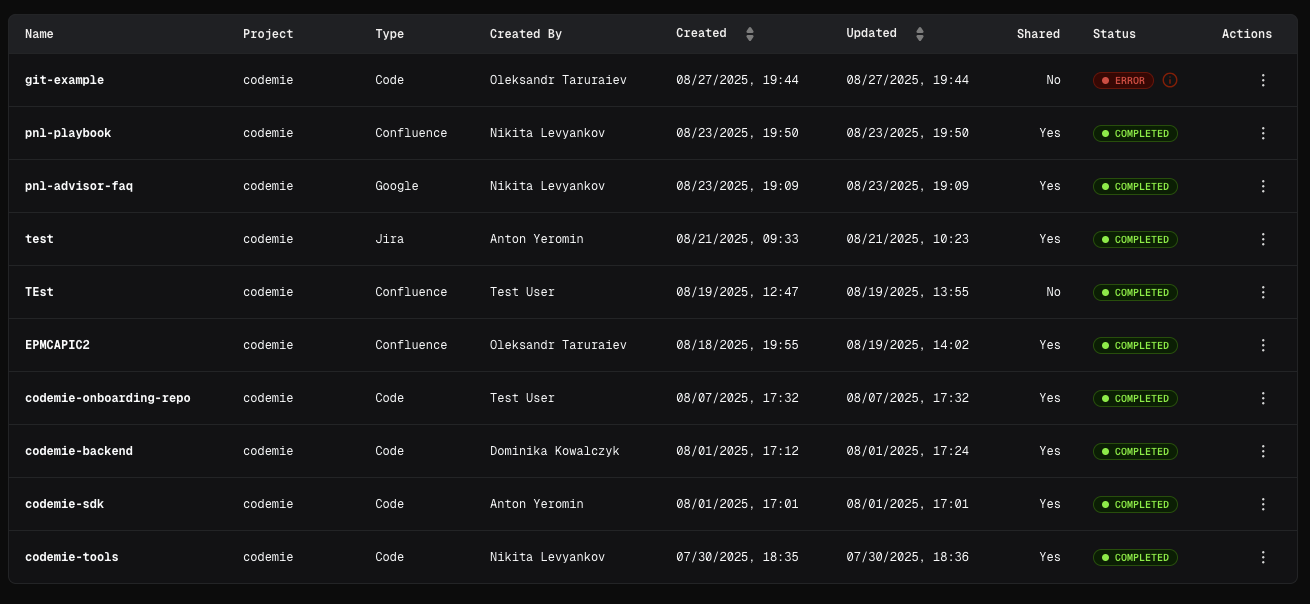
Error Handling for Git Data Sources
Errors can occur in the following cases:
- Invalid repository link: URL format is incorrect or repository doesn't exist
- Invalid token: Git integration credentials are expired or incorrect
- Incorrect branch link: Specified branch doesn't exist in the repository
For all these cases, after the data source is added and automatic reindex is created, a general error with exit code (128) will appear:
Now your Git repository is configured as a data source and ready to enhance your assistants with codebase knowledge.
Common Error Messages
Exit Code 128
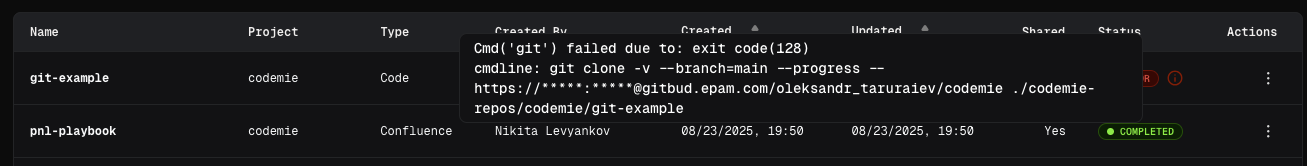
Cause: General Git operation failure
Common reasons:
- Repository not found or inaccessible
- Authentication failed
- Network connectivity issues
- Invalid branch name
Solutions:
- Verify repository URL is correct
- Check Git integration credentials are valid
- Ensure branch name exists in the repository
- Test repository access manually
- Review integration permissions
Connection Timeout
Cause: Cannot establish connection to Git server
Solutions:
- Check network connectivity
- Verify Git server is accessible
- Review firewall settings
- Try again after a few minutes
Permission Denied
Cause: Insufficient access to repository
Solutions:
- Verify integration has read access to repository
- Check repository visibility settings (public/private)
- Update integration credentials
- Request access from repository owner
Using Git Data Source in Assistants
After successfully creating and indexing your Git data source, you can connect it to any assistant to provide access to your codebase.
Adding Data Source to Assistant
- Navigate to Assistants section
- Click + Create Assistant or edit an existing assistant
- In the Data Source Context section, click the dropdown menu
- Select your Git data source from the list
- Save the assistant configuration
Now your assistant can access and analyze code from the indexed repository, enabling it to:
- Answer questions about code structure and implementation
- Explain functions, classes, and modules
- Suggest code improvements and refactoring
- Help with debugging and troubleshooting
- Provide codebase-specific recommendations
Your Git repository is now configured and ready to enhance your assistants with codebase knowledge.