AI/Run CodeMie Components Deployment
Overview
This section guides you through deploying the AI/Run CodeMie application stack on your GKE cluster. After completing infrastructure deployment, this phase installs all necessary Kubernetes components including:
- Core AI/Run CodeMie services (API, UI, MCP Connect, NATS Auth)
- Data layer (Elasticsearch, PostgreSQL via operators)
- Security & Identity (Keycloak, OAuth2 Proxy)
- Infrastructure services (Ingress controller, storage)
- Observability (Kibana, Fluent Bit)
- Optional LLM Proxy (for load balancing AI model requests)
The deployment uses Helm charts to install and configure all components in the correct order, ensuring proper dependencies and integration.
This phase assumes you have completed Infrastructure Deployment and have a running GKE cluster with network, storage, and security configured.
Application Stack Components
The AI/Run CodeMie application consists of multiple integrated components organized into functional categories. Understanding this architecture helps you plan the deployment sequence and troubleshoot issues effectively.
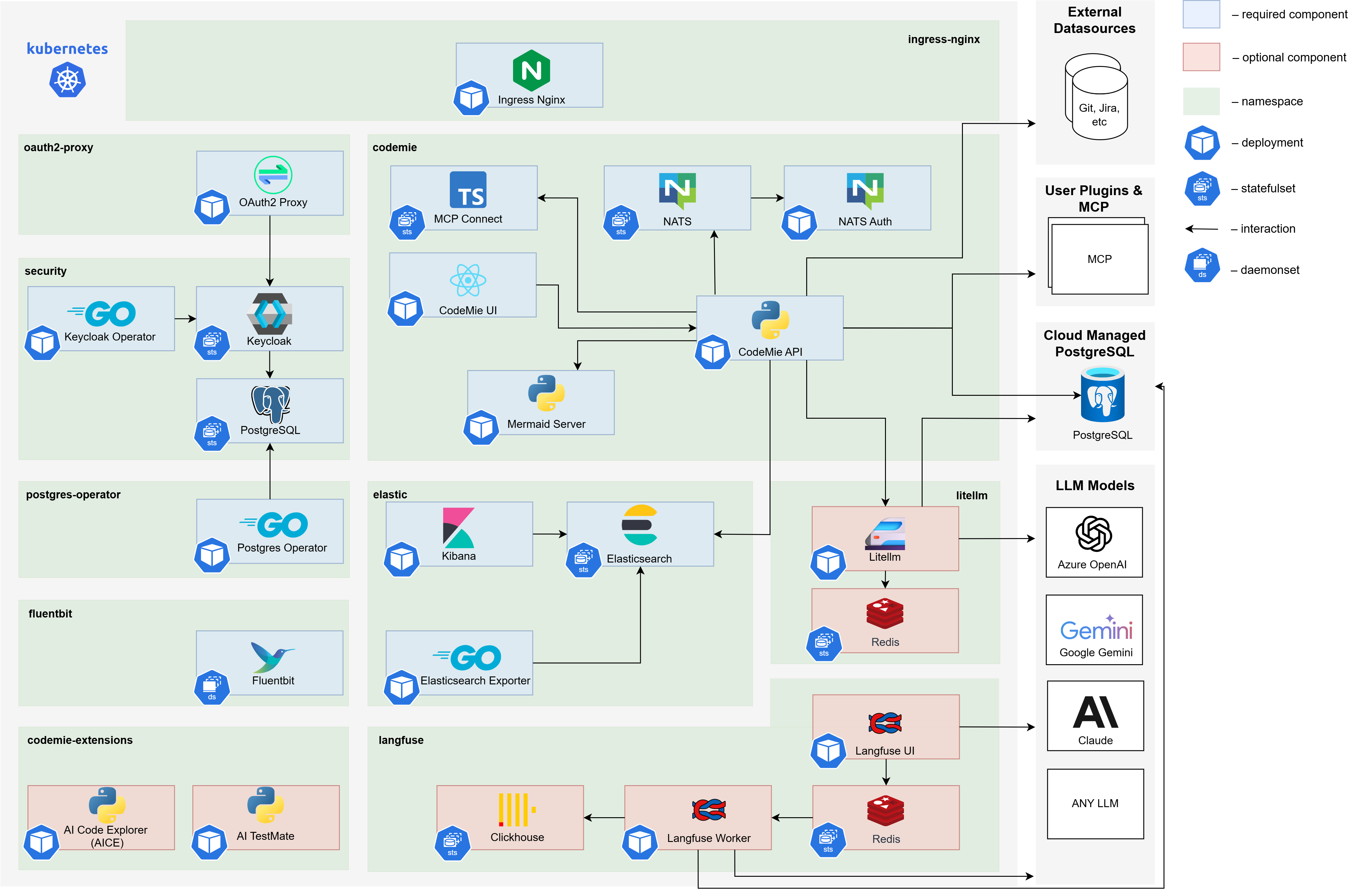
Core AI/Run CodeMie Services
Proprietary services that provide the main AI/Run CodeMie functionality:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CodeMie API | europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/.../codemie:x.y.z | Backend service handling business logic, data processing, and API operations |
| CodeMie UI | europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/.../codemie-ui:x.y.z | Frontend web application providing the user interface |
| NATS Auth Callout | europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/.../codemie-nats-auth-callout:x.y.z | Authentication and authorization service for NATS messaging (Plugin Engine component) |
| MCP Connect | europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/.../codemie-mcp-connect-service:x.y.z | Bridge enabling CodeMie to communicate with MCP servers |
| Mermaid Server | europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/.../mermaid-server:x.y.z | Diagram generation service for visualization in chats |
To find the latest release versions for CodeMie components:
bash get-codemie-latest-release-version.sh
# Use the version detection script with GCP credentials
bash get-codemie-latest-release-version.sh -c key.json
Make sure you logged in with key.json shared with you.
Note: Docker container versions match Helm chart release versions.
Data Layer Components
Database and storage services for application data:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticsearch | docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:x.y.z | Document storage, full-text search engine, and analytics platform |
| Kibana | docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:x.y.z | Visualization and exploration tool for Elasticsearch data and logs |
| PostgreSQL Operator | registry.developers.crunchydata.com/.../postgres-operator:x.y.z | Kubernetes operator for managing PostgreSQL database lifecycle |
| PostgreSQL | registry.developers.crunchydata.com/.../crunchy-postgres:x.y.z | Relational database for structured application data (managed via operator or Cloud SQL) |
Security & Identity Components
Authentication, authorization, and access control services:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Keycloak Operator | epamedp/keycloak-operator:x.y.z | Kubernetes operator for managing Keycloak lifecycle and configuration |
| Keycloak | quay.io/keycloak/keycloak:x.y.z | Identity and access management (IAM) server for user authentication |
| OAuth2 Proxy | quay.io/oauth2-proxy/oauth2-proxy:x.y.z | Reverse proxy providing authentication for web applications using OAuth2/OIDC |
Infrastructure Components
Foundational services for networking and storage:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nginx Ingress Controller | registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/controller:x.y.z | HTTP/HTTPS load balancer and reverse proxy for cluster traffic routing |
| GCP Storage Class | – | StorageClass for dynamic provisioning of GCP Persistent Disks |
Messaging Infrastructure (Plugin Engine)
Message broker for inter-service communication and plugin system:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NATS | nats:x.y.z | Lightweight, high-performance messaging system for microservices communication |
Observability Components
Logging, monitoring, and troubleshooting tools:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fluent Bit | cr.fluentbit.io/fluent/fluent-bit:x.y.z | Lightweight log processor and forwarder for centralized logging |
| Kibana Dashboards | – | Pre-configured dashboards for monitoring CodeMie metrics and usage |
Optional Components
Additional services for enhanced functionality:
| Component | Container Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LLM Proxy | – | Load balancer and router for AI model requests (supports multiple providers/models) |
Deployment Order
Components must be installed in the following sequence to satisfy dependencies:
- Infrastructure → Ingress Controller, Storage Class
- Operators → PostgreSQL Operator, Keycloak Operator
- Data Layer → Elasticsearch, PostgreSQL instances
- Security → Keycloak, OAuth2 Proxy
- Messaging → NATS
- Core Services → CodeMie API, UI, MCP Connect, NATS Auth
- Observability → Fluent Bit, Kibana
- Optional → LLM Proxy (if needed)
Prerequisites
Cluster Readiness
Ensure your GKE cluster is ready for component deployment:
- Infrastructure Deployed: Completed Infrastructure Deployment phase
- Cluster Access: kubectl configured and authenticated to GKE cluster
- Bastion/Jumpbox Access: Connected to Bastion Host (for private clusters) or have authorized network access
Configure Kubectl Access
Obtain kubectl credentials using the appropriate Terraform output command based on your cluster access type:
# For public clusters or clusters with authorized networks
# Use the command from Terraform outputs
# Parameter: get_kubectl_credentials_for_public_cluster
# For completely private clusters (access via Bastion Host)
# Use the command from Terraform outputs
# Parameter: get_kubectl_credentials_for_private_cluster
Verify cluster connectivity:
# Test cluster access
kubectl get nodes
# Check cluster information
kubectl cluster-info
Required Components
The following components will be installed during this phase if not already present:
- Nginx Ingress Controller: Routes external traffic to services
- GCP Storage Class: Provides persistent storage for stateful components
These components will be installed automatically if not already present in your cluster. Both scripted and manual deployment procedures include the necessary installation steps.
Repository and Access
Helm Charts Repository
Clone the Helm charts repository on your deployment machine (Bastion Host or local workstation):
git clone git@gitbud.epam.com:epm-cdme/codemie-helm-charts.git
cd codemie-helm-charts
Container Registry Credentials
Before deploying AI/Run CodeMie components, you need to set up authentication for the container registry.
Request Access: Ask the AI/Run CodeMie team to provide:
key.jsonfile (GCP service account credentials)- Service account email for pulling images from GCR
Create Namespace:
kubectl create namespace codemie
Configure Registry Secret:
Replace %%PROJECT_NAME%% with your project name and create the pull secret:
kubectl create secret docker-registry gcp-artifact-registry \
--docker-server=https://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev \
--docker-email=`<client_email from shared with you key>` \
--docker-username=_json_key \
--docker-password="$(cat key.json)" \
-n codemie
Verify Secret:
kubectl get secret gcp-artifact-registry -n codemie
The gcp-artifact-registry secret must be referenced in all AI/Run CodeMie component deployments: codemie-ui, codemie-api, codemie-nats-auth-callout, codemie-mcp-connect-service, and mermaid-server.
This is configured automatically in the values files:
imagePullSecrets:
- name: gcp-artifact-registry
Deployment Methods
Two deployment approaches are available depending on your needs:
Scripted Deployment (Recommended)
Automated deployment using the helm-charts.sh wrapper script:
- Best for: Standard deployments, quick setup, production environments
- Advantages: Automated dependency ordering, validation checks, consistent configuration
Manual Deployment
Step-by-step manual installation of each component:
- Best for: Custom configurations, learning the stack, troubleshooting
- Advantages: Full control over each component, easier to debug issues
Use Scripted Deployment for initial installations. Switch to manual deployment only if you need custom configurations or are troubleshooting specific issues.
Next Steps
After successful component deployment, proceed to Configuration to set up users, AI models, and complete the platform configuration.